Severe Toothache at Night: Causes & Emergency Tips
- Harkirat Aulakh
- Jan 22
- 5 min read
Severe Toothache at Night 7 Causes and When It s an Emergency
Severe toothache at night can be a distressing experience. The pain often feels more intense when you're trying to sleep. This can disrupt your rest and affect your overall well-being. If you’re dealing with a nighttime toothache, understanding the causes and practical tooth pain remedies can help you rest easier.
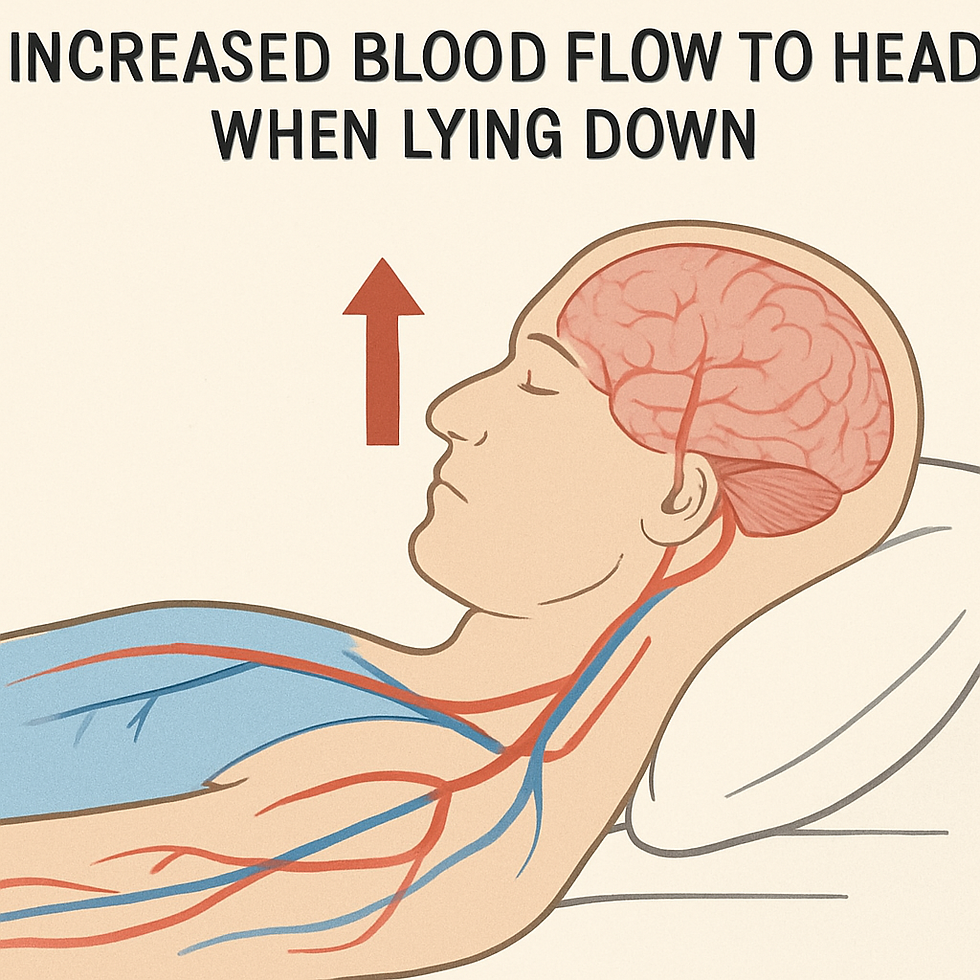
Understanding the causes of nighttime toothache is crucial. Common culprits include cavities, gum disease, and bruxism. These issues can worsen when lying down due to increased blood flow to the head.
Home remedies might offer temporary relief. However, persistent or severe tooth pain may signal a dental emergency. Knowing when to seek professional help is vital for your health.
This article explores the causes of severe toothache at night. It also provides tooth pain remedies and guidance on when to consult a dentist. Stay informed to protect your dental health.

Why Does Toothache Get Worse at Night?
Toothache often intensifies at night, making it harder to sleep. One reason is the position we sleep in. Lying down causes more blood to flow to the head. This increased flow can amplify the pain. For some people with severe tooth pain, these nighttime factors can make every throb feel stronger.
Another factor is the absence of distractions at night. During the day, activities can divert your attention from the pain. At night, the quiet can make the pain more noticeable and uncomfortable.
Several reasons contribute to nighttime toothache worsening:
Increased blood flow when lying down
Lack of distractions
Decreased levels of endorphins at night
Decreasing your head's elevation can help. Try using an extra pillow to reduce blood flow to the head. This may ease some of the pain and promote better sleep.
7 Common Causes of Severe Toothache at Night
Several factors can trigger severe toothache at night. One of the primary culprits is tooth decay. Cavities can worsen over time, especially when left untreated. This decay can lead to significant pain, particularly at night when sensitivity may increase.
Gum disease is another common cause. Inflamed gums can cause throbbing pain that becomes more apparent during quiet nighttime hours. The inflammation often intensifies when lying flat, making it harder to ignore.
A cracked or damaged tooth can also cause severe pain at night. Changes in temperature, such as breathing cool air, can exacerbate this discomfort. The pain is often sharp and piercing.
Bruxism, or teeth grinding, usually occurs at night. This condition can lead to aching teeth and jaw discomfort. Stress frequently contributes to bruxism, compounding the problem.
Sinus infections are less obvious sources of tooth pain. They affect the upper teeth and can mimic a severe toothache. Lying down can increase sinus pressure, worsening tooth pain.
Dental abscesses result from untreated infections. They can cause intense pain and swelling, especially at night. Without treatment, the infection may spread, leading to serious complications.
Impacted wisdom teeth can also cause nighttime toothache. They exert pressure on other teeth, often causing severe discomfort. This pressure can lead to persistent pain that worsens when resting.
Common causes of nighttime toothache include:
Tooth decay
Gum disease
Cracked or damaged tooth
Bruxism (teeth grinding)
Sinus infections
Dental abscess
Impacted wisdom teeth
If one or more of these conditions describe your symptoms, seeking dental advice promptly is wise. Understanding these causes can help you take steps to alleviate pain and find effective solutions.

Home Remedies for Nighttime Toothache Relief
Finding relief from severe tooth pain at night can be challenging. However, several home remedies can help alleviate discomfort temporarily. The tooth pain remedies below can help during the night, though they are temporary.
One effective method is rinsing your mouth with warm salt water. This solution can reduce inflammation and act as a natural disinfectant. It's a simple yet effective remedy.
A cold compress applied to the cheek can help numb the affected area. This reduces swelling and soothes pain. Ensure not to apply ice directly to the skin.
Over-the-counter pain relievers can also offer temporary relief. Medications like ibuprofen or acetaminophen can help manage the pain until you can see a dentist.
Additional remedies include:
Clove oil for its numbing properties
Elevating your head with an extra pillow
Avoiding sweet or acidic foods
For those who prefer natural remedies, clove oil is a great option. It contains eugenol, which numbs pain effectively. Apply a small amount onto a cotton ball and place it on the sore tooth.
These remedies are temporary fixes. They may help manage the pain but are not substitutes for professional dental care. Visiting a dentist should be prioritized if the pain persists.
When Is Severe Tooth Pain an Emergency?
Severe tooth pain at night can sometimes be a sign of a dental emergency. Understanding the symptoms that require urgent care is crucial for your oral health.
Persistent pain, especially if accompanied by swelling or fever, should not be ignored. Such symptoms may indicate an infection or abscess. These conditions require prompt dental attention to prevent complications.
Additionally, if you experience difficulty swallowing or breathing, seek emergency care immediately. These can be serious signs of infection spreading beyond the tooth.
Signs that indicate a dental emergency include:
Severe, constant toothache
Noticeable facial swelling
Fever along with tooth pain
Trouble swallowing or breathing
If any of these symptoms occur, it's important to contact a dentist or visit an emergency care center without delay. Quick intervention can prevent further health issues and relieve pain effectively.
What to Do Before You See a Dentist
Before you can see a dentist, there are steps you can take to alleviate nighttime toothache and manage severe tooth pain. These remedies provide temporary relief and prepare you for your dental visit.
Firstly, rinse your mouth gently with warm salt water. This helps reduce inflammation and cleans the area. Secondly, apply a cold compress to the outside of your cheek where the pain is most intense. This will help numb the pain and reduce swelling.
Here's a quick list of actions to consider:
Rinse with warm salt water
Apply a cold compress
Take over-the-counter pain relievers
Keep your head elevated while lying down
Taking these steps can ease your discomfort and prevent further irritation until professional care is available.
How to Prevent Nighttime Tooth Pain
Preventing nighttime toothache involves maintaining good oral hygiene and making healthy lifestyle choices. Regular dental check-ups help identify and address potential problems before they worsen. Implement daily habits to keep your teeth in top condition.
Consider the following preventive steps:
Brush and floss twice daily
Limit sugary foods and drinks
Use fluoride toothpaste
Wear a night guard if you grind your teeth
By integrating these practices into your routine, you'll reduce the likelihood of severe tooth pain disrupting your sleep. Proper dental care is essential to avoid unwelcome discomfort during the night.
Final Thoughts: Don't Ignore Severe Toothache at Night
Ignoring severe toothache at night can worsen dental issues and lead to serious health problems. It's crucial to address symptoms promptly to prevent complications.
Schedule a dental visit if tooth pain persists. Early treatment can improve your oral health and eliminate painful nights. Taking action now will ensure your peace of mind and well-being.

Comments